Unit 11 – Agile Architectures
Open Agile Architecture Practitioner Certification
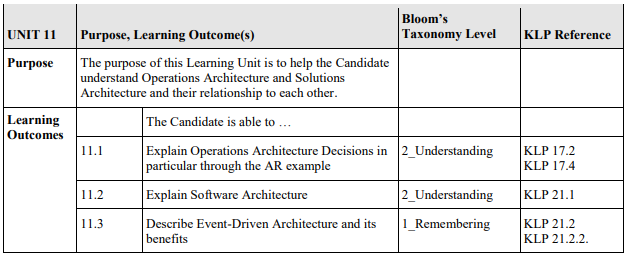
11.1 Explain Operations Architecture Decisions in particular through the AR example
Outward view that specifies the operational capabilities that products need.
challenge - trial and error not possible when costs of change are too high
AR Apparel Retailer
- Automating non-essential decsisions could be done incrementally.
- You need great operational design and great people.
- Culture is fast decision-making, but not at the expense of operating excellence.
- Improvements are deployed incrementally.
- The Japanese Meeting - Having a five minute chat about the days objectives before opening.
- Continuous improvement is ingrained as part of the culture.
- Directors visit stores to explain culture to the staff.
11.2 Explain Software Architecture
- Modern software systems are composed of multiple components.
- Decompose the components of the architecture, and how they interact together
- Also concerned with non-functional requirements
- Processes of the team are also important
- A software architect needs to have strong soft-skills
11.3 Describe Event-Driven Architecture and its benefits
An architecture that centers around events:
- Better handling of state, concurrency, and time
- The Real World is Event-Driven
- Loose coupling and strong autonomy - Losser coupling between producer and consumer
- Focus on Behavior and changeability
- Better operability with events
- Good operability is reached by strong logging practices.
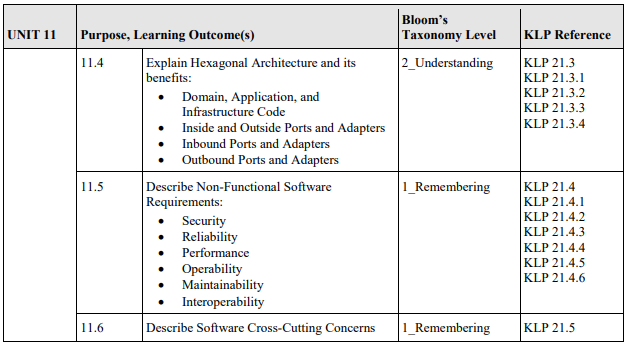
11.4 Explain Hexagonal Architecture and its benefits:
Hexagonal achitecture decouples the domain, application, and infrastructure logic. Inbound ports and adapters on the left side, outbound on the left
Domain, Application, and Infrastructure Code
Domain Code - code dealing with domain concepts and relate behavior
Application Code - Code interacting with the external world
Inside and Outside Ports and Adapters
The "domain core" of an application must be protected from the outside. Application and infrastructure logic change very rapidly.
- Domain code must be isolated from the rest of the code.
- Domain code should be runnable as a stand-alone library, capable of executing all domain logic in-memory.
- Ports - boundaries of the domain
- Adapters - An implementation that adheres to the protocol exposed by the port
Hexagonal architecture makes heavy us of interface/implementation decoupling mechanisms.
Inbound Ports and Adapters
Entry points to the domain. the domain reacts to requests coming from inbound ports. Inbound adapter is something like an API, GUI, or CLI.
Outbound Ports and Adapters
Exit points invoked from the domain. Driven by the domain to perform infrastructure tasks. Outbound adapter examples are DB repository, Message-Oriented Middleware, IAM systems, and other external systems the domain depends on.
11.5 Describe Non-Functional Software Requirements:
Security
Auth, monitoring, audit logs, data security, integrity, vulnerability
Reliability
Probability of failure-free software in a specified time in a given environment.
- Maturity
- Decreasing the failure rate of software
- Mitigation of negative side effects that change can introduce
- Recoverability
- Minimizing duration to get system back up and running
- Fault-tolerance
- Continue operating properly with a failure in one of its components
Performance
- Scalability
- Cope with increased load
- Performance
- Throughput and latency
- Efficiency
- Quantity of resources used by the app to process its tasks
Operability
- Observability
- Expose high-level observation metrics of health, state, context
- Documentation
- Provide good documentation and be well-understood to be production ready
- Deployability
- Ease of deploying a new version of software in a target environment
Maintainability
Capacity of software to be modified.
- Testability
- Validate software behavior against acceptance criteria
- Coupling, Modularity, and Stability
- Coupling - dependencies between components of a system
- Modularity - topology of the architecture with number of components dependent on a particular component
- Stability - Ability of a product to avoid side effects from changes
Interoperability
Ability to exchange data and use common protocols to do so.
11.6 Describe Software Cross-Cutting Concerns
There are many cross-cutting concerns that go through the different NFRs:
- Language choices
- Testing strategy
- Persistence of data
- Session handling
- Business rules
- Load balancing and fault-tolerance
- Error handling